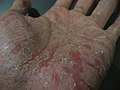
Dyshidrosis
| Dyshidrosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Recurrent vesicular palmoplantar dermatitis (RVPD),[1][2][3] acute vesiculobullous hand eczema,[4] dyshidrotic dermatitis,[5] dyshidrotic eczema,[6] pompholyx,[a] cheiropompholyx,[a] podopompholyx[a] |
 | |
| The characteristic vesicles of dyshidrosis on a finger | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Itchy blisters on the palms of the hands and bottoms of the feet[8] |
| Complications | skin thickening[9] |
| Usual onset | Often recurrent[10] |
| Duration | Heal over 3 weeks[9][10] |
| Causes | Unknown[10] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms[10] |
| Differential diagnosis | Pustular psoriasis, scabies[9] |
| Treatment | Avoiding triggers, barrier cream, steroid cream, antihistamines[9][10] |
| Frequency | ~1 in 2,000 (Sweden)[9] |
Dyshidrosis is a type of dermatitis characterized by itchy vesicles on the palms of the hands and bottoms of the feet.[8] Blisters are generally one to two millimeters in size and heal over three weeks.[9][10] However, they often recur.[10] Redness is not usually present.[9] Repeated attacks may result in fissures and skin thickening.[9] The cause of the condition is not known.[10]
Etymology
The condition was named dyshidrosis by the British dermatologist William Tilbury Fox in 1873. Giving the condition its first clinical description, he presented it as "a disordered condition of the sweat-follicles and the sweat-function... which is, as a rule, diagnosed as eczema, but is a separate and distinct affair... I have termed the disease dysidrosis [sic], because nature seems to have a difficulty in getting rid of the secreted sweat, which remains to distend the follicles, and to macerate the tissues."[11] His theory that the condition was related to sweat was observed to be unproven as early as 1885,[12] and subsequent research on multiple occasions has shown an absence of relation to the sweat glands.[13]
Signs and symptoms
The characteristics of dyshidrosis are:
- Itchiness of the palms or soles, followed by the sudden development of intensely itchy small blisters on the sides of the fingers, the palms or the feet.[14]
- These blisters are often described as having a "tapioca pudding" appearance.[15]
- After a few weeks, the small blisters eventually disappear as the top layer of skin falls off.[9][16][17]
- These eruptions do not occur elsewhere on the body.[9]
- The eruptions may be symmetrical.[18]
-
Advanced stage of dyshidrosis on the fingers
-
Palmar dyshidrosis
-
Advanced stage of palmar dyshidrosis on the palm showing cracked and peeling skin
-
Advanced stage of dyshidrosis on the foot.
-
Rim of scale on the palmar surface of the thumb from a resolving dyshidrotic flare
Causes
Whilst the exact causes of the condition are currently unknown,[10] its triggers may include food allergens from a wide range of foods, including tuna, tomato, pineapple, chocolate, coffee, and spices among others,[16], physical or mental stress, frequent hand washing, or metals.[16] A number of studies have implicated balsam of Peru.[16] A 2013 study found that dyshydrosis on the hands increased among those allergic to house dust mites, following inhalation of house dust mite allergen.[19] Id reaction and irritant contact dermatitis are also possible causes.[20]
Diagnosis
Dyshidrosis is diagnosed clinically by gathering a patient's history and making observations.[10] Allergy testing and culture may be done to rule out other problems.[10] Severity of symptoms can also be assessed using the dyshidrotic eczema area and severity index (DASI), although it was designed for clinical trials and is not typically used in practice.[21]
Treatment
Avoiding triggers may be useful, as may be the application of a barrier cream or wearing of gloves.[9] Treatment is generally made with steroid cream,[22] although this can be dangerous in the long term due to the side effect of thinning of the skin, which is particularly troublesome in the context of hand dyshidrosis due to the amount of toxins and bacteria the hands typically come in contact with. [10] High strength steroid creams may be required for the first week or two.[9]
In especially acute and severe cases, systemic steroids can be taken orally;[18] the immunosuppressive drug tacrolimus, or PUVA therapy may also be tried.[9][10] Dapsone (diamino-diphenyl sulfone), an antibacterial, has been recommended for the treatment of dyshidrosis in some chronic cases.[23]
Antihistamines such as Fexofenadine may be used to help with the itching.[24][10] Potassium permanganate dilute solution soaks are popular, used to "dry out" the vesicles[25] and kill off superficial Staphylococcus aureus,[26] but they can be very painful and undiluted may cause significant burning.[27]
Alitretinoin (9-cis-retinoic acid) has been approved for prescription in the UK. It is specifically used for chronic hand and foot eczema.[28][29][30] It is made by Basilea of Switzerland (BAL 4079).
Epidemiology
A study of 20,000 randomly-selected individuals in Gothenburg, Sweden in 1988 found 2% of male respondents and 3% of female respondents to have dyshidrosis, and that it comprised 5% of cases of hand eczema of any type.[31] A study of 6300 pediatric patients in Turkey in 2006 found 1% to have dyshidrosis.[32]
See also
- Dermatitis herpetiformis – a similar condition caused by celiac and often mistaken for dyshidrosis.
- Epidermolysis bullosa – a genetic disorder that causes similar, albeit more severe, symptoms to those of dyshidrosis.
Notes
References
- ^
Scotelaro-Alves, Hugo Guimarães; Fernandes, Nurimar Conceição; Ramos-e-Silva, Marcia (3 Jan 2019). "Clinical profile of recurrent vesicular palmoplantar dermatitis in children and adolescents". Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology. 12. Dove Medical Press: 23–28. doi:10.2147/CCID.S150778. PMC 6322509. PMID 30655684.
Recurrent vesicular palmoplantar dermatitis (RVPD) is the current and more accurate terminology for the condition that was previously referred to as dyshidrosis or 'pompholyx'.
- ^ S., Mrudula; Nandakishore, Thokchom; Kongbam, Linda; Valsalan, Bhavya; V., Nischith; Ralte, Lalthlamuana (23 February 2023). "Recurrent vesicular palmoplantar dermatitis: a clinical study in children and adolescents". International Journal of Research in Dermatology. 9 (2): 73–77. doi:10.18203/issn.2455-4529.IntJResDermatol20230454. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ Al Khalifa, Nayla; Raees, Mazen; Khalifa, Salman; Al Juffairi, Eman (23 January 2024). "Pediatric Recurrent Vesicular Palmoplantar Dermatitis Presenting with Pyrexia: A Case Report". Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports. 8. Fortune Journals: 13–15. ISSN 2575-9655. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ "Pompholyx". Patient. 2014-02-26. Archived from the original on 3 August 2016. Retrieved 11 August 2016.
- ^ a b Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ^ "Dyshidrosis". Merriam-Webster Online. Merriam-Webster. 2014. Archived from the original on 15 April 2014. Retrieved 14 April 2014.
- ^ a b "What Is Atopic Dermatitis? Fast Facts". NIAMS. November 2014. Archived from the original on 27 July 2016. Retrieved 11 August 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Lofgren, SM; Warshaw, EM (December 2006). "Dyshidrosis: epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and therapy". Dermatitis: Contact, Atopic, Occupational, Drug. 17 (4): 165–81. doi:10.2310/6620.2006.05021. PMID 17150166.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Colomb-Lippa, D; Klingler, AM (July 2011). "Dyshidrosis". Journal of the American Academy of Physician Assistants. 24 (7): 54. PMID 21748961.
- ^ Tilbury Fox, William (27 September 1873). "Clinical Lecture on Dysidrosis: An Undescribed Eruption". British Medical Journal. 2 (665): 365–366. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.665.365. PMC 2294466. PMID 20747210.
- ^ Robinson, Andrew Rose (1885). A Manual of Dermatology. New York: D. Appleton & Company. p. 252. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ Storrs, Frances J (December 2007). "Acute and recurrent vesicular hand dermatitis not pompholyx or dyshidrosis". JAMA Dermatology. 143 (12): 1578–1580. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.12.1578. PMID 18087011. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ Shelley, W. B. (1953-09-01). "Dysidrosis (pompholyx)". AMA Archives of Dermatology and Syphilology. 68 (3): 314–319. doi:10.1001/archderm.1953.01540090076008. ISSN 0096-5979. PMID 13079297.
- ^ Bielan, Barbara (1996-04-01). "Dyshidrotic eczema". Dermatology Nursing. 8 (2). Archived from the original on 2017-04-02.
- ^ a b c d Veien, Niels K. (2009-07-01). "Acute and recurrent vesicular hand dermatitis". Dermatologic Clinics. 27 (3): 337–353, vii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2009.05.013. ISSN 1558-0520. PMID 19580928.
- ^ Lofgren, Sabra M.; Warshaw, Erin M. (2006-12-01). "Dyshidrosis: epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and therapy". Dermatitis: Contact, Atopic, Occupational, Drug. 17 (4): 165–181. doi:10.2310/6620.2006.05021. ISSN 1710-3568. PMID 17150166.
- ^ a b Perry, Adam D.; Trafeli, John P. (2009-05-01). "Hand Dermatitis: Review of Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment". The Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine. 22 (3): 325–330. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2009.03.080118. ISSN 1557-2625. PMID 19429739.
- ^ Schuttelaar ML, Coenraads PJ, Huizinga J, De Monchy JG, Vermeulen KM (2013). "Increase in vesicular hand eczema after house dust mite inhalation provocation: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study" (PDF). Contact Dermatitis. 68 (2): 76–85. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2012.02172.x. hdl:11370/69c0f80d-e6f3-4dff-ad75-aadf46b5aaa4. PMID 23046099. S2CID 4609200.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, James (2016). "8". Dermatology Secrets Plus. Elsevier. pp. 70–81. ISBN 978-0-323-31029-1.
- ^ Vocks, E.; Plötz, S. G.; Ring, J. (1999-01-01). "The Dyshidrotic Eczema Area and Severity Index – A score developed for the assessment of dyshidrotic eczema". Dermatology. 198 (3): 265–269. doi:10.1159/000018127. ISSN 1018-8665. PMID 10393450. S2CID 22978226.
- ^ "eMedicine – Dyshidrotic Eczema: Article by Camila K Janniger". Archived from the original on 2007-07-07. Retrieved 2007-07-10.
- ^ "Vesicular hand dermatitis". Archived from the original on 2010-03-30. Retrieved 2010-04-07.
- ^ Diepgen, Thomas L.; Agner, Tove; Aberer, Werner; Berth-Jones, John; Cambazard, Frédéric; Elsner, Peter; McFadden, John; Coenraads, Pieter Jan (2007-10-01). "Management of chronic hand eczema". Contact Dermatitis. 57 (4): 203–210. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.01179.x. ISSN 1600-0536. PMID 17868211. S2CID 34639884.
- ^ BIRT AR (March 1964). "Drugs for Eczema of Children". Can Med Assoc J. 90 (11): 693–4. PMC 1922428. PMID 14127384.
- ^ Stalder JF, Fleury M, Sourisse M, et al. (1992). "Comparative effects of two topical antiseptics (chlorhexidine vs KMn04) on bacterial skin flora in atopic dermatitis". Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 176: 132–4. PMID 1476027.
- ^ Baron S, Moss C (February 2003). "Caustic burn caused by potassium permanganate". Arch. Dis. Child. 88 (2): 96. doi:10.1136/adc.88.2.96. PMC 1719457. PMID 12538301.
- ^ Ruzicka T, Lynde CW, Jemec GB, Diepgen T, Berth-Jones J, Coenraads PJ, et al. (April 2008). "Efficacy and safety of oral alitretinoin (9-cis retinoic acid) in patients with severe chronic hand eczema refractory to topical corticosteroids: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial" (PDF). Br. J. Dermatol. 158 (4): 808–17. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08487.x. PMID 18294310. S2CID 205256947. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-02-18. Retrieved 2019-02-05.
- ^ Bollag W, Ott F (1999). "Successful treatment of chronic hand eczema with oral 9-cis-retinoic acid". Dermatology (Basel). 199 (4): 308–12. doi:10.1159/000018280. PMID 10640839. S2CID 35358182.
- ^ Ruzicka T, Larsen FG, Galewicz D, Horváth A, Coenraads PJ, Thestrup-Pedersen K, Ortonne JP, Zouboulis CC, Harsch M, Brown TC, Zultak M (December 2004). "Oral alitretinoin (9-cis-retinoic acid) therapy for chronic hand dermatitis in patients refractory to standard therapy: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial". Arch Dermatol. 140 (12): 1453–9. doi:10.1001/archderm.140.12.1453. PMID 15611422.
- ^
Meding, B.; Swanbeck, G. (17 May 1989). "Epidemiology of different types of hand eczema in an industrial city". Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 69 (3): 227–233. doi:10.2340/0001555569227233 (inactive 2024-05-16). PMID 2566226. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of May 2024 (link) - ^ Tamer, Emine; Ilhan, Mustafa N.; Polat, Muhterem; Lenk, Nurdan; Alli, Nuran (10 July 2008). "Prevalence of skin diseases among pediatric patients in Turkey". Journal of Dermatology. 35 (7): 413–418. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2008.00495.x. PMID 18705828. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
External links
- Pompholyx at DermNet NZ (New Zealand Dermatological Society Incorporated)