Daewoo Lanos
| Daewoo Lanos (T100) | |
|---|---|
 Daewoo Lanos (T100) 3-door hatchback | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Daewoo |
| Also called |
|
| Production | 1997–2002 (Daewoo) 1997–2020 (CKD and license-built models) |
| Assembly | |
| Designer | Giorgetto Giugiaro at italdesign |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Subcompact car (B/C) |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | Front-engine, front-wheel-drive |
| Platform | GM T platform |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,520 mm (99.2 in) |
| Length | 4,074 mm (160.4 in) (hatchback) 4,235 mm (166.7 in) (sedan) 4,247 mm (167.2 in) (panel van) |
| Width | 1,678 mm (66.1 in) |
| Height | 1,432 mm (56.4 in) 1,908 mm (75.1 in) (panel van) |
| Curb weight | 990–1,177 kg (2,182.6–2,594.8 lb) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Daewoo Cielo ZAZ Tavria (for ZAZ models) |
| Successor | Daewoo Kalos |
The Daewoo Lanos is a compact / sedan car produced by the South Korean manufacturer Daewoo from 1997 to 2002, and thereafter produced under license agreements in various countries worldwide. It has also been marketed as the Daewoo Sens, ZAZ Sens and ZAZ Lanos in Ukraine, Doninvest Assol and ZAZ Chance in Russia, FSO Lanos in Poland, or Chevrolet Lanos in Ukraine, Russia, and Egypt.
It was designed by Giorgetto Giugiaro and initially featured three body styles: three-door and five-door hatchbacks and a four-door sedan. The Lanos was designated the T100 model code at launch; the T150 code applies to the updated models introduced in 1999. In 2006, a panel van version, produced in Ukraine by ZAZ, was also introduced. The Daewoo Lanos was designed to replace the Daewoo Nexia in the Daewoo line-up and was itself replaced by the Daewoo Kalos.
Production of the Daewoo Lanos ended in 2020.[citation needed]
Development[edit]
In 1992, Daewoo dissolved its joint-venture with General Motors, and simultaneously a decision was made to independently develop replacements for the contemporary Daewoo Motors products, based on older General Motors models. The Lanos development programme was formally started in autumn 1993, with the goal to create a car to replace Daewoo Nexia as Daewoo's small family car.[6]
The project began with a comparative study of competing models from 20 different manufacturers, with Toyota Tercel, Opel Astra and Volkswagen Golf identified as most competitive. Four design studios were commissioned to deliver clay models presenting their ideas for the new model's styling. Giorgetto Giugiaro's design was chosen, and Italdesign was commissioned to develop the car's final outside and interior styling. The technical side of the project was conducted simultaneously by Daewoo's development centre Korea, as well as suppliers and contractors who were involved in developing particular components. This included AC Rochester (engine components), Delco Chassis Division (brakes, including ABS), GM Powertrain (automatic transmission), Italdesign (body, structural analysis, electrics, prototype construction), PARS Passive Rückhaltesysteme GmbH (airbags) and Porsche (vehicle concept – research, structural analysis, suspension and brake components, and experimental production supervision).[6]
By the end of 1995, 150 prototypes were built (providing for three body styles). The development programme involved extensive testing in a multitude of locations. Safety tests included high-speed stability and durability testing in England, and brake testing on the Großglockner in Austria. Low-temperature testing was conducted in Canada, Sweden (Arjeplog), and Russia (Moscow, Khabarovsk) while high-temperature tests took place in the US (Death Valley), Oman (Nizwa), Australia (Alice Springs), Spain (Barcelona), and Italy (Nardò). The programme was completed in a remarkable time of only 30 months from the approval to the commencement of large-scale production of the Lanos sedan for the Korean market. European-market production began in 1997.[6]
-
2001 Daewoo Lanos (T150) sedan
-
Daewoo Lanos (T150) 5-door hatchback
-
2001 Daewoo Lanos (T150) Sport 3-door hatchback
-
2001 Daewoo Lanos (T150) Sport 3-door hatchback
Technical details[edit]
The cars were equipped with E-TEC I4 with single cam and twin cam engines ranging from 1.5 L (1498 cc 86HP) SOHC to 1.6 L (1598 cc 106HP) DOHC. In the UK and many countries of Europe (like Italy, France or Austria) there are also E-TEC models 1.4 (1349 cc 75HP) and 1.6 (1598 cc 106HP). The suspension is built upon that of a Daewoo Nexia, as used in Vauxhall/Opel Astra Mk2 GTE.
On the mechanical side, all Lanos versions shared the same parts with a few exceptions. Differences between the 1.6 DOHC engine version and the other versions were:
- The 1.6 DOHC versions were equipped with 256mm front brake rotors and 22mm master cylinders rather than the 236mm disks and 20mm master cylinder found on the other versions with the less power engines.
- The 1.6 DOHC versions were equipped with D16 long ratio transmissions which had a slightly bigger final gear ratio compared to the D16 short ratio found on the other versions with the less power engines.
- The 1.6 DOHC versions were equipped with stiffer front springs to compensate for the heavier engine in comparison to both SOHC engines found in the other versions.
The four models available were S, SE, SE Plus, SX, and later, the SPORT model. The S was the base model and did not include many standard features (like a CD player or power windows). The SE was just a small step up from the S base model. However, the SX model usually included a CD, radio, and cassette player along with power windows, a power side mirror, and fog lights. A few select SX models even came with a sun-roof, though not many did. In the Lanos's later years, the SE and SX models were dropped and replaced with a new trim line called the SPORT (2001–2002). The SPORT included several features similar to the SX, but also included red/black leather seats and a metallic silver dash trim. Also, the SPORT model had window controls located on the doors rather than the center console (like in the previous trim lines).
-
Interior (higher model)
-
Interior (lower model)
-
Interior with automatic transmission
-
Interior with automatic transmission
Marketing and production[edit]
Outside South Korea, the Lanos has been produced in Poland (from 1997 to 2008), Ukraine (from 1998 to 2017), Russia (briefly produced, from 1998 to 2000), Egypt (from 1998 to 2020). Most of the initial production was made using complete knock down (CKD) kits, which were supplied to FSO (in Poland), ZAZ (in Ukraine), TagAZ (in Russia), Daewoo Motors Egypt and GM Egypt (in Egypt) and VIDAMCO (in Vietnam).
Central and Eastern Europe[edit]
In Poland, the Fabryka Samochodów Osobowych (FSO) plant in Warsaw began the production of the Lanos in 1998. Since January 2005, after the takeover of Daewoo by General Motors, the Lanos produced in Poland started to be sold under the brand name of FSO. It was produced until 2008, but only with the pre-facelift external design.
From 2002, ZAZ equipped some of the kits with a domestic MeMZ-307 engine and sold this version under the Daewoo Sens name; this practice continues with the start of full-scale production of model T150. In December 2004, ZAZ adopted the Lanos chassis for full-scale production and installed new welding and painting lines.[7] From March 2009, the updated version is called ZAZ Lanos (internal model T150).[8] The engines are still supplied by GM Daewoo, although a Chinese-developed engine from Chery Automobile has been fitted and there are plans to build the 1.6 L engine at the MeMZ plant.[9]
In 2005, General Motors contracted with ZAZ to provide Ukrainian-assembled Lanos models for the Ukrainian and Russian markets, to be imported duty-free, thanks to an international agreement, and sold through the GM dealer network. Sales of the Chevrolet Lanos sedan commenced in Russia in November 2005.[10] The Chevrolet brand was utilized to compete effectively with the Renault Logan. From July 2009, it is marketed in Russia as ZAZ Chance.[11]
In 2006, a panel van variant of the ZAZ Lanos was introduced.[12]
-
2006 Chevrolet Lanos (T150) sedan
-
ZAZ Lanos sedan (Ukraine)
-
ZAZ Lanos Panel Van
-
ZAZ Lanos Panel Van
Egypt[edit]
Since late 1998, the Daewoo Motor Egypt factory in Cairo started the assembly of the Daewoo Lanos in both 4 door and 5 door shells with the 1.5 SOHC engine.[13] The hatchback version was called "Juliet".[14] The 4 door was available in two versions:
- The SX model which was fully loaded with all options plus an automatic transmission
- The S model that had A/C, power steering and radio cassette plus a manual transmission
The 5 door version of the Lanos (AKA Juliet) came with full options as the SX trim but with manual transmission.
Near the end of year 2000 the Lanos was introduced with a different rear end design and a face lifted front (different front bumper and grill). It was called "Lanos II" in this particular market. An SE version came with all the options plus the manual transmission. The automatic transmission version was stopped shortly after the introduction of the "Lanos II".
Between mid 2000 and 2001 the factory produced an even more frugal 4 door version of the Lanos II with no options at all but a cassette and those were sold by the Egyptian ministry of defense to army officers with a decently low price compared to the car's value at that time.
The facelifting also included the five-door Juliet to have the same changes as the 4 door version on the front but on the rear it only had a different design tail-lights and bumper rather than a wholly different design rear end like the sedan, the production of the Juliet stopped within 2005.
In November 2008, GM Egypt started producing the Chevrolet Lanos in 6th of October City, from Ukrainian supplied kits.[15]
Sales[edit]
Australia and North America[edit]
The Lanos was finally phased out after the 2002 model year, superseded worldwide by the Daewoo Kalos. Daewoo ceased operations in North America. After GM took over Daewoo to become GMDAT, Chevrolet began importing the Daewoo Kalos, rebadged as the Aveo, to North America beginning with MY 2004. However, the Lanos continues to be sold in Mexico and Latin America.
The 2001 and 2002 models follow a recent trend among cars intended to be sold in many markets, in that their rear lamps are asymmetric, with the fog lamp and reverse lamp occupying complementary spots on the driver's side and passenger side respectively; consequently, the rear lamps differ between left- and right-hand drive examples.
Ukraine[edit]
In Ukraine, the Lanos has been the best-selling car since at least 2006,[16] and until 2014 (except 2012),[17] being produced by the local manufacturer ZAZ under its own brand (starting from 2005).[18] Over the years, 364,000 cars were bought in Ukraine.[19]
Safety[edit]
In Australia, the 1997–2003 Daewoo Lanos was assessed in the Used Car Safety Ratings 2006 as providing "worse than average" protection for its occupants in the event of a crash.[20]
Europe: models received the following European New Car Assessment Program (Euro NCAP) 1998 ratings:[21]
- Adult Occupant:


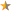

 , score 17
, score 17 - Pedestrian:



 , score 11 (pre-2002 rating)
, score 11 (pre-2002 rating)
In crash tests conducted by ANCAP in 1998 to Euro NCAP protocols RHD Lanos 3dr hatchback showed poor performance, scoring 0.31 out of 16 in offset front crash test and 6.98 of 16 in side impact test.[22][23] Russian magazine Autoreview tested LHD Chevrolet Lanos T150 sedan built by ZAZ in 2006. It scored 10.5 of 16 points in offset front crash test.[24]
References[edit]
- ^ Satyam. "Welcome to GMArabia.com". GMEgypt.com. Archived from the original on 9 August 2010. Retrieved 19 July 2010.
- ^ "Welcome to Lanos Website". AboulFotouh.com. Archived from the original on 5 March 2010. Retrieved 19 July 2010.
- ^ "UkrAVTO Corporation. ZAZ". UkrAvto.ua. Archived from the original on 11 December 2010. Retrieved 22 October 2010.
- ^ "UkrAVTO Corporation. FSO". UkrAvto.ua. Archived from the original on 24 April 2009. Retrieved 22 October 2010.
- ^ "History". GMVietnam.com.vn. Archived from the original on 18 April 2012. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ a b c "Internetowy Klub Lanosa" (in Polish). Archived from the original on 17 March 2010.
- ^ "Corporation "UkrAvto" and CJSC "ZAZ" start full-scale production of "Lanos" car". AvtoZAZ.com. 15 December 2004. Archived from the original on 27 January 2005.
- ^ "ZAZ cars: buy Ukrainian - support native makers". AvtoZAZ.com. 31 March 2009. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ "Lanos received a more powerful engine from Forza" (in Russian). Autobigmir.net. 10 May 2011. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ "Home Page". Chevrolet Russia. Archived from the original on 24 November 2005. Retrieved 19 December 2013.
- ^ "Chevrolet Lanos turns into Chance". AvtoZAZ.com. 7 July 2009. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ "New! Lanos-pickup". AvtoZAZ. 1 June 2006. Archived from the original on 4 November 2006.
- ^ "About Us". Aboul Fotouh. Archived from the original on 14 October 2011. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ "Products". Abou Ghaly Motors. Archived from the original on 20 February 2007.
- ^ "Lanos will be produced in Egypt" (in Russian). InfoCar.com.ua. 27 October 2008. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ "Ukraine Full Year 2011: ZAZ Lanos leader, two Ladas on podium". Best Selling Cars Blog. 16 January 2012. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- ^ "Ukraine Full Year 2014: Toyota and Geely on top, market down 54%". Best Selling Cars Blog. 24 March 2015. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- ^ "Ukraine". Best Selling Cars Blog. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- ^ "Визначено найбільш продаваний автомобіль в Україні за останні 17 років / Новое Время". 19 May 2017. Archived from the original on 19 May 2017. Retrieved 3 January 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Used Car Safety Ratings: 2006 Update (PDF), Lan Transport NZ, Australian Transport Safety Bureau, June 2006, p. 10, ISSN 1176-9890, archived from the original (PDF) on 27 January 2007 – via Vic Roads
- ^ "Euro NCAP - Daewoo Lanos 1998 crash test". Euro NCAP. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
- ^ "ANCAP crash test results - Daewoo Lanos 3 dr 1998". NZ Transport Agency. Archived from the original on 20 October 2011. Retrieved 9 October 2011.
- ^ "ANCAP crash test results - Daewoo Lanos 1998". NZ Transport Agency. Archived from the original on 20 October 2011. Retrieved 9 October 2011.
- ^ "Краш-тест: Chevrolet Lanos" (in Russian). Autoreview. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
External links[edit]
- Lanos & Sens homepage (Russian)
- Aboul Fotouh website (Arabic)
- Chevrolet Lanos website (Egypt)


















